Honeybees: The Buzz About Saving the Planet
Honeybees are found in temperate and tropical regions of the world. The most common species is the western honeybee, Apis mellifera, which is native to Europe and Asia but has been introduced to most other parts of the world.
Honeybees can fly up to 20 miles per hour, they can pollinate up to 1,000 flowers in a day, and a single honeybee hive can produce up to 60 pounds of honey in a year. Talk about a miracle maker!
Interestingly, honeybees have five eyes: three simple eyes on their forehead and two compound eyes on the sides of their head. But that’s not the only fascinating feature of honeybees. They actually communicate with each other through a variety of dances.
As a fellow beekeeper, I’m sure you’d love reading more incredible facts about honeybees.
Description and Characteristics of Honeybees
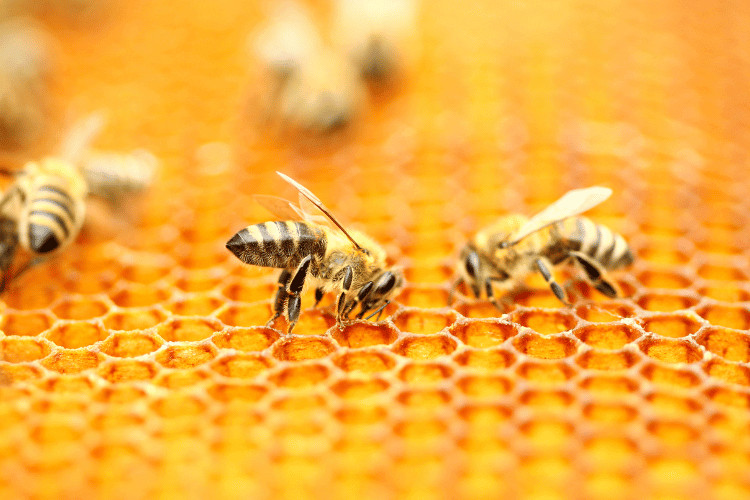

Honeybees are eusocial insects, meaning that they live in colonies with a strict division of labor. The colony is typically made up of one queen, several hundred to several thousand worker bees, and a few hundred drones.
The queen is the only fertile female in the colony and she lays all of the eggs. The worker bees are female and do all of the work of the colony, including gathering food, building the hive, and caring for the young.
The drones are male bees and their only role is to mate with the single queen of the colony.
Honeybees are important pollinators of plants. They collect nectar and pollen from flowers, and they transfer pollen from one flower to another as they fly. This helps to fertilize the flowers and produce fruit and seeds.
Honeybees also produce honey, which is a sweet, edible substance made from the nectar of flowers. Honey is used by humans for food, as well as for making other products such as candles and cosmetics.
What Is a Honeybee’s Purpose?
The purpose of a honeybee is to help the colony survive and thrive. Honeybees are social insects that live in colonies with a strict division of labor.
Each bee has a specific role to play in the colony, and all of the bees work together to ensure the success of the group. Sometimes this system fails and results in a colony collapse disorder.
In addition to honey production, honeybees pollinate plants and care for the queen and young bees. Honeybees are essential to our ecosystem, and their decline is a major concern.
Honeybees’ Habitat and Foraging Preferences
You can find honeybees in a variety of habitats, including forests, meadows, and gardens. They prefer habitats that have a variety of flowers, as this provides them with a source of nectar and pollen. Honeybees are also attracted to water sources, such as streams and ponds.
Honeybees forage for nectar and pollen within a radius of about 2 miles from their hive. However, they can travel up to 5 miles in search of food. The specific plants that they forage on depends on the time of year and the region.
In the spring, they typically forage on early-blooming flowers, such as dandelions and clover. In the summer, they forage on a wider variety of flowers, including roses, sunflowers, and lavender. In the fall, they forage on late-blooming flowers, such as asters and goldenrod.
Honeybees are attracted to flowers that have a strong scent and a lot of nectar. They also prefer flowers that are easy to land on and have a long corolla (the tube-like part of the flower).
Honeybees use their long tongues to suck nectar from flowers. They also collect pollen on their legs and fur, which they then take back to the hive.
Honeybee’s Life Cycle, Mating, and Nesting
The lifespan of a honeybee varies depending on its role in the colony. Queens can live for up to five years, while worker bees live for about six weeks. Drones only live for a few weeks.
Life Cycle
The honeybee life cycle has four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
- Egg: The queen lays eggs in cells in the honeycomb. The eggs are fertilized by the drones, and they hatch into larvae after about three days.
- Larva: The bee larvae are fed by the female workers for about six days. They grow rapidly during this time, and they spin a cocoon around themselves when they are ready to pupate.
- Pupa: The pupa is the stage between the larva and the adult bee. The pupa is enclosed in the cocoon, and it undergoes a transformation during this stage. The adult bee emerges from the cocoon after about two weeks.
- Adult: The adult bee has four wings and a long tongue. It can fly and collect nectar and pollen from flowers. The adult bee also has a stinger that it can use to defend itself.
Mating
Honeybees mate during a mating flight. The queen swiftly leaves the hive and flies up into the air. That’s where she is met by drones from other hives.
The drones then compete for the chance to mate with the queen, and the strongest drone wins. Not many people know that the queen mates with several drones during her mating flight, but hey, facts are facts!
Nesting
Honeybees build their nests in hives. The hive is made up of honeycombs, which are made of wax. The honeycombs are where the bees store their honey and pollen. The hive is also where the bees raise their young.
Importance of Honeybees in Ecosystems and Agriculture
Honeybees are essential pollinators, and their decline is a major concern for both the environment and agriculture.
Pollination
As pollinators, honeybees help to fertilize plants by transferring pollen from one flower to another. This is essential for the reproduction of many plants, including fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
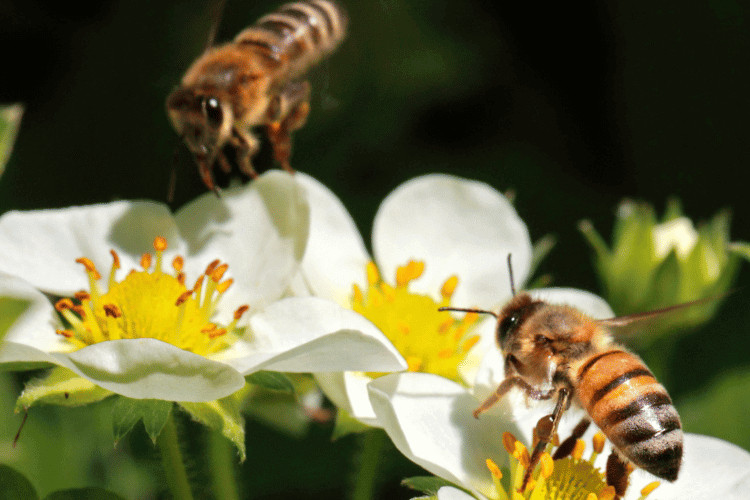

In fact, honeybees are responsible for pollinating about one-third of the food crops that we eat. This means that without honeybees, our food supply would be severely disrupted.
Maintaining Plant Diversity
In addition to their importance in agriculture, honeybees also play a vital role in ecosystems. They help to maintain plant diversity by pollinating a wide variety of plants. They also help to control pests by pollinating plants that produce insecticidal compounds.
For example, honeybees help to pollinate apple trees, which are a major crop in many countries. Without honeybees, apple production would be significantly reduced.
Increasing Agricultural Yield
Honeybees also help to pollinate almonds, which are another important crop. In California, almonds are the state’s leading agricultural export. Honeybees, literally, save almond production singlehandedly.
Improving Air Quality
Honeybees are also important for the environment in other ways. They help to improve air quality by releasing enzymes that break down pollutants.
Create Thriving Habitats
These busy bees also help to create habitats for other insects and animals.
For example, honeybees help to create habitats for butterflies by pollinating butterfly-friendly plants. This helps to ensure the survival of butterflies, which are also important pollinators.
Common Questions About Honeybees
What Do Honeybees Eat?
Honeybees eat two main foods: nectar and pollen.
- Nectar: Nectar is a sweet liquid that bees get from flowers. It’s the main source of energy for honeybees. Honeybees collect nectar in their honey sacs and transport it back to the hive.
- Pollen: Pollen is a powdery substance produced by flowers. It’s the main source of protein for honeybees. Honeybees collect pollen on their bodies and legs and transport it back to the hive.
Honeybees also eat honey, which is a sweet substance made by honeybees from nectar. Honey is stored in the hive and is used as a food source during the winter months.
In addition to nectar, pollen, and honey, honeybees may also eat other foods, such as:
- Water
- Bee bread
- Royal jelly
- Insect larvae
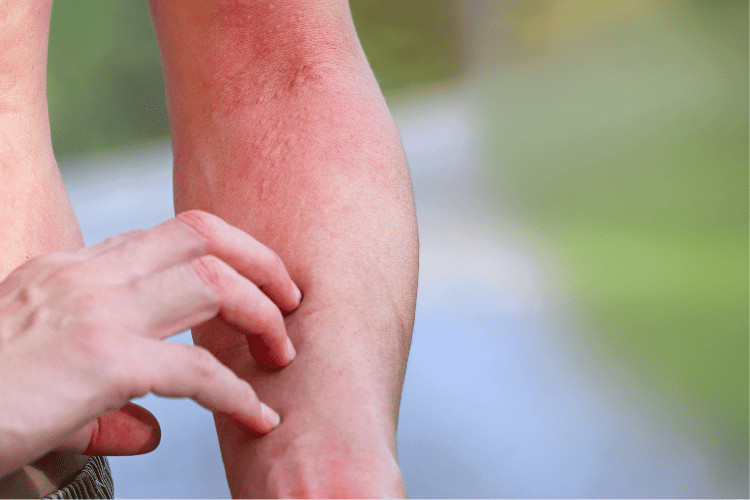
Are Honeybees Dangerous?
Honeybees aren’t inherently dangerous. They’re docile creatures that only sting in self-defense. However, honeybees can be dangerous if they are provoked or feel threatened.
Honeybees have a barbed stinger that they use to defend themselves. When a honeybee stings, the stinger gets stuck in the skin, and the bee’s abdomen tears off. This is fatal to the bee, but it can also be painful and dangerous for the person who is stung.
The bee venom can cause pain, swelling, and redness at the sting site. In some cases, it can also cause allergic reactions, such as hives, difficulty breathing, and even anaphylaxis.
If you’re stung by a honeybee, it’s important to remove the stinger as quickly as possible. You can do this by scraping it off with your fingernails or a credit card. You should also wash the sting site with soap and water.
If you experience any allergic reactions to the sting, such as hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face or tongue, you should seek medical attention immediately.
What Size Are Honeybees?
Honeybees are about 1/2 inch (12.7 mm) long. However, their size can vary depending on the species.
The largest honeybee species is the giant honeybee, which can grow up to 1.5 inches (38 mm) long. And the smallest honeybee species is the dwarf honeybee, which can grow up to 0.5 inches (12.7 mm) long.
How to Identify Honeybees?
Honeybees are one of the most common bee species in the world. They’re easily recognizable by their black and yellow stripes. However, there are a few other things you can look for to help you identify honeybees.
Here are some features of honeybees:
- They are about 1/2 inch (12.7 mm) long.
- They have a black and yellow striped body.
- The black stripes are on the abdomen, while the yellow stripes are on the thorax.
- They have two pairs of wings and a pair of antennae.
- They have a barbed stinger that they use to defend themselves.
How to Attract Honeybees?
Here are some tips on how to attract honeybees to your garden:
- Plant a variety of flowers that bloom throughout the year. Some good choices for attracting honeybees include asters, black-eyed Susans, and bluebells.
- Plant flowers that are native to your area.
- Plant flowers in full sun.
- Avoid using pesticides.
- Provide a water source for the bees.
- Leave some dead wood in your garden.
- If you have a beehive, make sure it’s located in a safe place where it won’t be disturbed.
- Avoid using herbicides. Herbicides can kill the plants that honeybees need for food.
- Plant flowers at different heights. This will help to attract a wider variety of bees.
- Place flowers near each other. This will make it easier for the bees to travel from flower to flower.
- Mulch your garden. Mulch helps to keep the soil moist and cool, which is important for bees.
Conclusion
As beekeepers, we are well aware of the economic importance of honeybees. They give us honey, beeswax, royal jelly, and propolis. This is in addition to pollination services, pest control, improved air quality, and habitat creation.
In 2019, a study found that honeybees could save the US agricultural industry $15 billion per year by pollinating crops. This saves farmers money and helps to ensure a stable food supply.
Additionally, honeybees are important for the environment. They help to maintain plant diversity and control pests, which in turn helps to create healthy ecosystems and protects biodiversity.

Joseph Davis
My goal is to show that anyone can take up beekeeping and it can be a very rewarding hobby. I strive to share my experiences and answer any questions you may have.
